Executive Summary
Multicast
Troubleshooting
Executive Summary
Multicast is a technology that allows traffic to scale across a network. InformaCast puts a single multicast audio stream on a network that any endpoint can request, which allows InformaCast to scale a broadcast to thousands of devices quickly and efficiently.
Back to Top
How Multicast Is Routed?
InformaCast has no special requirements for how multicast is enabled on a network. Singlewire recommends that you use your network vendor’s best practices and design considerations.
Multicast is typically routed with Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) that is deployed in either sparse or dense mode:
- Dense Mode. Traffic is put out to the entire network distribution tree and pruned back until it flows to only the segments of the tree that require it.
- Sparse Mode. A rendezvous point is configured in the network that is the root of all multicast traffic to be sent. The multicast traffic is only sent to network segments that request the traffic.
InformaCast will work with either mode.
Back to Top
What About Multicast On The WAN?
Many Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) network providers will not route multicast traffic on their networks. For WAN links where your circuit provider will not route your multicast, you have two options:
- GRE tunnels
- Singlewire Paging Gateway
GRE Tunnels
Using your network, you can configure a GRE tunnel to carry your multicast traffic from the location where the InformaCast server is located to the remote site(s). The only traffic that needs to traverse these GRE tunnels is the multicast traffic you might want to route. The tunnels do not need to create a full mesh between sites; they only need to be configured from the hub location to the spoke location(s).
Cisco has detailed documentation to configure multicast over GRE tunnels
The advantages of using GRE tunnels to route multicast are:
- Administration. All configurations are done on network devices. This is a mature technology that is well documented and supported by network vendors. Once the initial configuration is completed, the ongoing administration is minimal.
- Cost. Because there will already be a router at both the hub and spoke locations, there is no additional hardware or software costs.
Singlewire Paging Gateway
The Singlewire Paging Gateway will allow a lower bit rate unicast audio stream to be sent from an InformaCast server at one location to a Paging Gateway across a WAN that will not route multicast. The Paging Gateway can then turn the unicast audio stream it received from the InformaCast server at the other location into multicast on the local LAN segment. For more information, please contact your Singlewire Territory Manager: sales@singlewire.com.
The advantages of using a Paging Gateway to get audio over a non-multicast-enabled WAN are:
- Bandwidth. The unicast audio stream that travels over the WAN is a lower bit rate codec. At the remote site LAN, the traffic is turned back into G.711 µlaw multicast.
- Deployment. As long as the LAN(s) route multicast, there is no need to configure multicast routing over the WAN.
Back to Top
How Do Phones Request Multicast Audio?
To get InformaCast audio to phones, the phones must request it. The phones use Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) to request the audio stream from the network. While most networks default to IGMPv2, the newer models of phones use IGMPv3. If newer phones are being deployed, be sure to enable the newer protocol version on network devices.
Back to Top
Where Can I Get More Information?
For more information than the contents of this document provide, work directly with your network vendor and consulting partner for detailed information.
Back to Top
Multicast
InformaCast uses multicast to route the audio portion of a broadcast and requires that your network route multicast traffic. Multicast routing allows a sender to put one packet on the wire and route that packet across the network to many recipients.
Design Recommendations
Multicast is typically routed with Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM). InformaCast has no requirements for how multicast routing is enabled on the network, except that it be routed on the network from the source to the destinations that request it. Because of this, Singlewire recommends configuring your network’s multicast routing based on your network vendor’s best practices. If you have a Cisco network, use Cisco best practices.
Back to Top
Example Configurations, Guides, and Tools
The following table provides guides and resources for more information on configuring multicast on your network.
| RESOURCE | DESCRIPTION |
|---|
| Quick Start Guide |
Cisco IP Multicast Quick Start Configuration that provides concise configuration examples
|
|
Design Guides
|
Cisco Design Zone for IP Multicast for access to the AVVID SRND for Multicast Design
|
|
Multicast Troubleshooting
|
Cisco IP Multicast Troubleshooting Guide
|
|
IGMP Snooping
|
Cisco CGMP and IGMP Snooping documentation
|
|
GRE Tunnels
|
Cisco Multicast over a GRE Tunnel (for when a WAN carrier will not route multicast)
|
|
Singlewire Paging Gateway
|
Singlewire solution for lower bit rate unicast over a WAN link (for when a WAN carrier will not route multicast)
|
|
Testing Tool
|
Singlewire tool to send and receive multicast traffic, which can be used to verify and troubleshoot multicast routing
|
|
Protocol Analyzer
|
Wireshark download link, which can be used to view network traffic for troubleshooting
|
Back to Top
Assistance With Multicast Configuration
Network design and multicast configuration is outside the scope for which Singlewire can provide support. It is recommended that you work with your network vendor or partner. If you have a Cisco network, you can work with the Cisco TAC or locate a local Cisco Partner. The following table provides Cisco resources for configuration help.
Back to Top
Understanding InformaCast Traffic Flow
It is important to note that the only piece of traffic that travels through the network via multicast routing is the audio portion of a broadcast. All signaling traffic and the text portion of a broadcast are done with unicast HTTP. The diagram below outlines the traffic that occurs during an InformaCast broadcast that contains both text and audio.
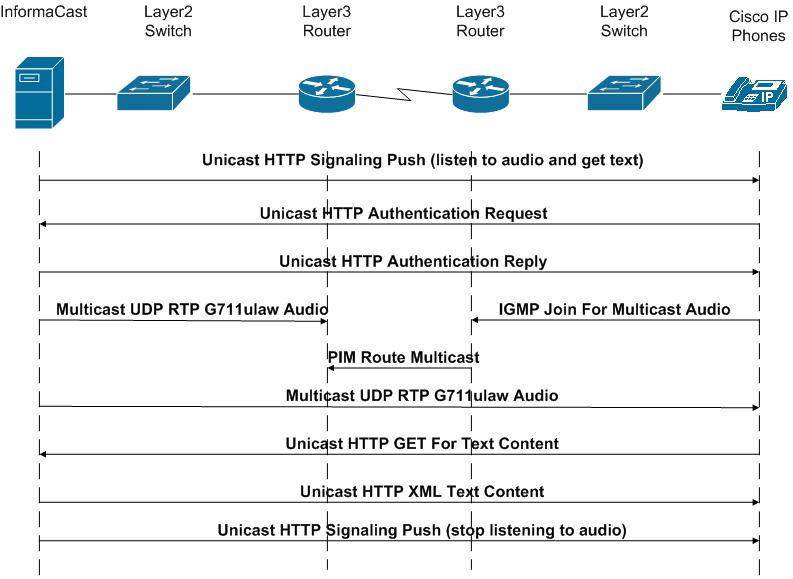
Back to Top
Troubleshooting
The following symptoms will occur during an InformaCast broadcast if multicast routing is not enabled:
- Text displays on the phone’s screen, but no audio is heard through the phone
- A streaming icon displays on the phone’s screen
- A phone’s Speaker and Mute lights illuminate
- 7900 series phones makes a “bloop” noise
When troubleshooting multicast issues on your network, you have a few options available to you:
- Investigating multicast routing with Singlewire’s Multicast Testing Tool
- Obtaining and analyzing network traffic captures
- Ensuring that PIM is configured on all Layer 3 interfaces
- Using GRE tunnels or the Singlewire Paging Gateway to route audio across WAN links that don’t support multicast
- Disabling IGMP snooping
- Ensuring that the network uses IGMPv3 if newer phones are deployed
Back to Top
Multicast Testing Tool
Singlewire offers a Multicast Testing Tool to help troubleshoot and isolate multicast routing issues. Download the Multicast Testing Tool
The Multicast Testing Tool allows you to act as a server sourcing a multicast stream from different points on the network. It can also be run as a client to be placed on various points on the network. By having the Multicast Testing Tool put multicast traffic on the network and having clients look for that traffic, you can narrow down multicast routing configuration issues.
The Multicast Testing Tool can also be used to control two Cisco IP phones: one to source multicast audio and one to receive it. For instance, you could use two phones on the same switch to verify that multicast is working on the LAN, and phones on different network segments to locate where multicast may not be routing.
Back to Top
Network Traffic Capture
Once you are familiar with the traffic flow created by InformaCast, you can use a protocol analyzer to sniff the traffic on the network to see that all communications happened as expected.
Obtain a Network Traffic Capture
Use the following steps to obtain a network traffic capture from a phone to determine if multicast traffic is routing to that network segment.
Step 1. Download and install a protocol analyzer like Wireshark on a PC that’s attached to a phone on your network on which you want to obtain a traffic capture.
Step 2. Open and log into your Communications Manager’s administrative interface. The Cisco Unified CM Administration page appears.
Step 3. Go to Device | Phone. The Find and List Phone page appears.
Step 4. Use the dropdown menus and fields to locate the phone attached to the PC on which you downloaded Wireshark. Your results will appear below the fields.
Step 5. Select the phone attached to your PC with Wireshark on it. The Phone Configuration page for that phone appears.
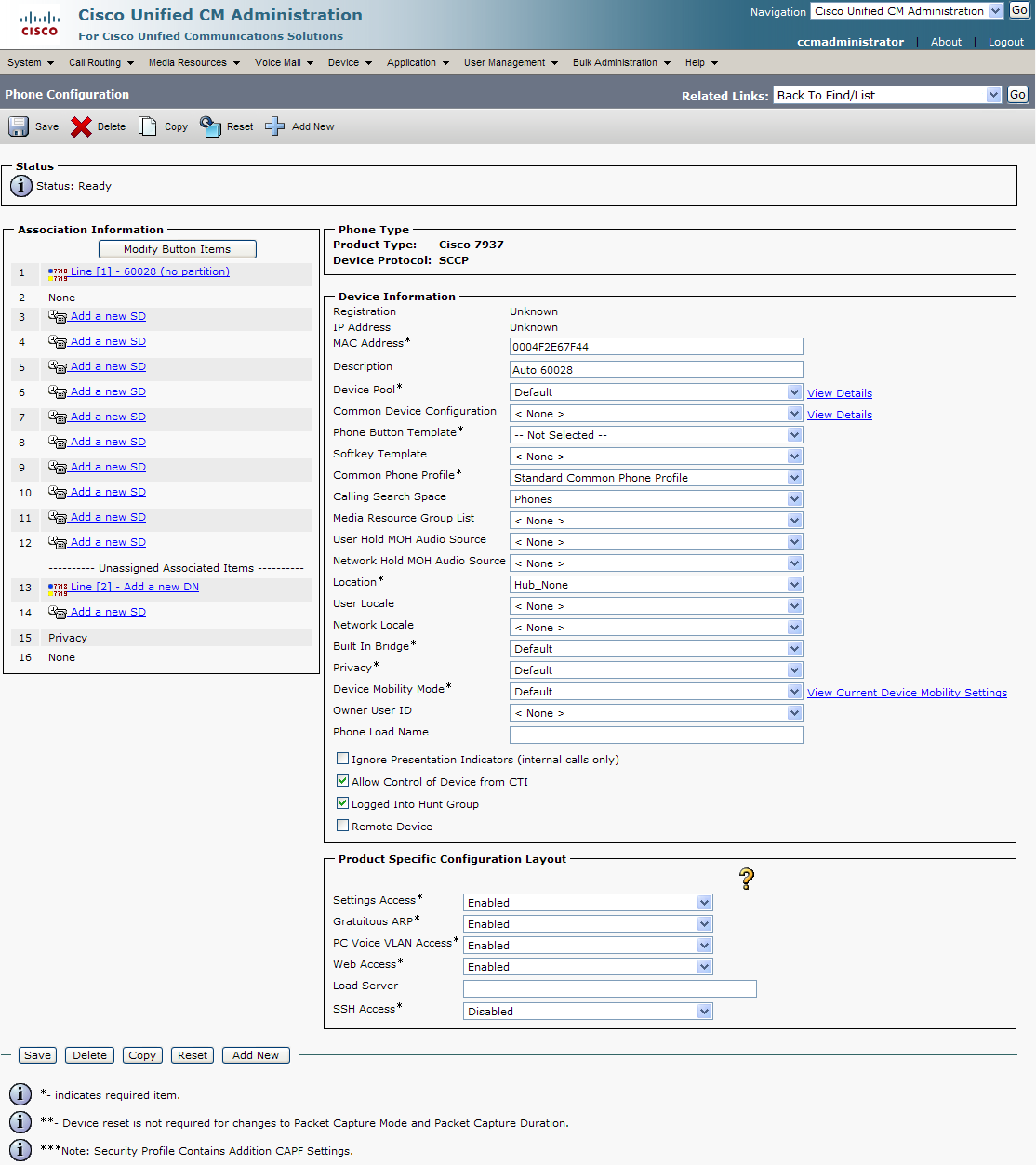
Step 6. Scroll down to the Product Specific Configuration Layout area.
Step 7. Make sure that both the Web Access and Span to PC Port dropdown menus have Enabled selected.
Step 8. Click the Reset button.
Step 9. Start Wireshark.
Step 10. Send an InformaCast broadcast to the phone attached to the PC with Wireshark on it.
Step 11. Wait until the broadcast has finished and stop the network traffic capture.
Read a Network Traffic Capture
After you obtain a network traffic capture, you need to know how to read it. When analyzing a network traffic capture, look for the following:
- A unicast HTTP command from InformaCast to the phone to join the multicast group
- Successful authentication
- An IGMP join from the phone to the multicast group
- A multicast audio stream
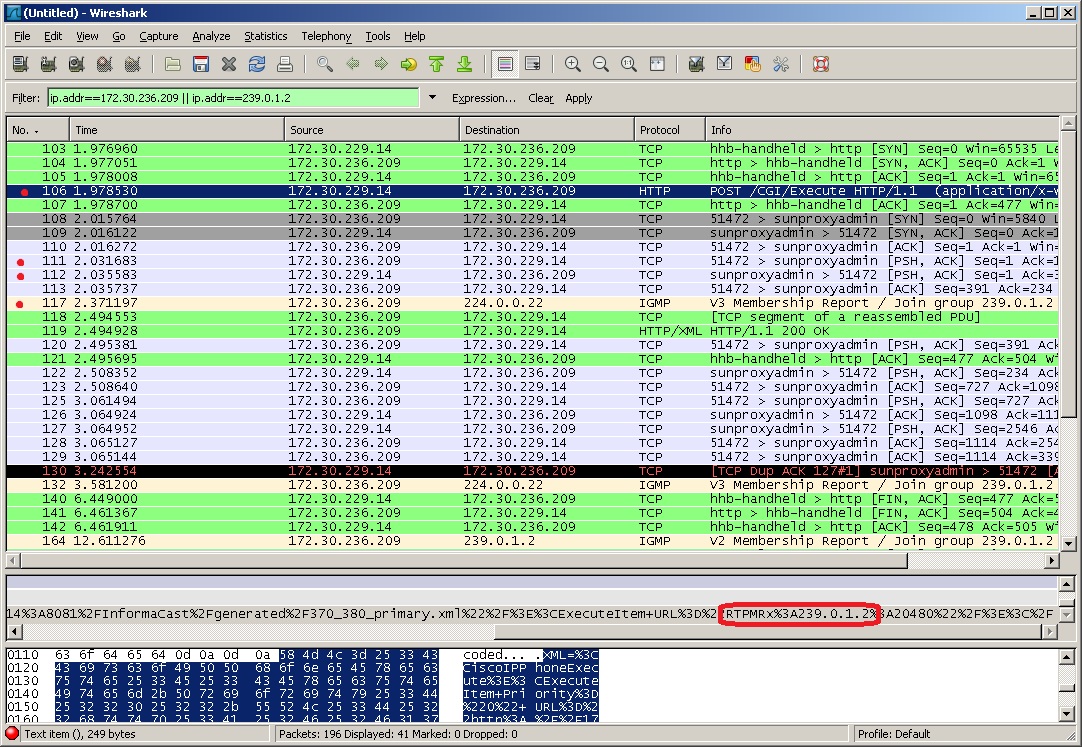
When there is no multicast audio present, InformaCast audio will not play through a phone, and you’ll notice the following things in your traffic capture (reference with the graphic on the following page):
- Frame 106. InformaCast pushes the unicast HTTP command to a phone to listen to audio and get text. In the middle pane, the multicast IP address to listen for is circled in red.
- Frame 111. The phone makes a unicast HTTP authentication request. The protocol doesn’t show as HTTP because the communication took place on port 8081. You can view the contents of the packet for the actual data or decode as HTTP.
- Frame 112. InformaCast replies in unicast HTTP to the authentication request as OK.
- Frame 117. The phone makes an IGMP join request for a multicast audio stream.
- Frame 164. There is a timestamp nine seconds after the IGMP join, but no multicast traffic is seen in the capture. Thus, multicast is not routing and no audio will be received at the phone.
Each of the things to look for are marked with red in the following graphic.
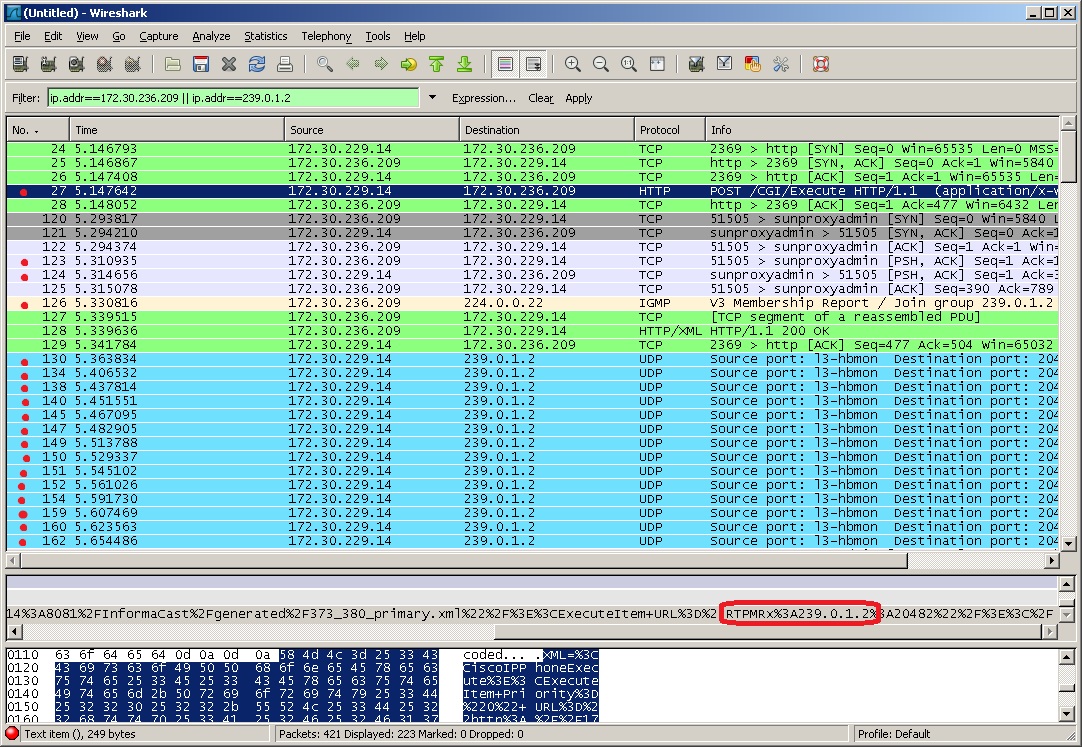
When there is multicast audio present, InformaCast audio plays through phone, and you’ll notice the following things in your traffic capture (reference with the graphic on the following page):
- Frame 27. InformaCast pushes the unicast HTTP command to a phone to listen to audio and get text. In the middle pane, the multicast IP address to listen for is circled in red.
- Frame 123. The phone makes a unicast HTTP authentication request. The protocol doesn’t show as HTTP because the communication took place on port 8081. You can view the contents of the packet for the actual data or decode as HTTP.
- Frame 124. InformaCast replies in unicast HTTP to the authentication request as OK.
- Frame 126. The phone makes an IGMP join request for a multicast audio stream.
- Frames 130 - 62 (plus more). The multicast UDP is present. Audio should have played through the phone.
Each of the things to look for are marked with red in the following graphic.
Back to Top
PIM Configured On All Layer 3 Interfaces
For audio broadcast traffic to route from a source (InformaCast) to a destination (IP phones) every Layer 3 interface in between must have PIM configured. If the switches on the network are also providing Layer 3, then PIM must be enabled on the VLANs configured on those switches providing Layer 3 functionality. PIM is deployed in either sparse or dense mode, and InformaCast will work with either.
The following graphic shows PIM enabled on all Layer 3 interfaces between the IP phones and InformaCast.
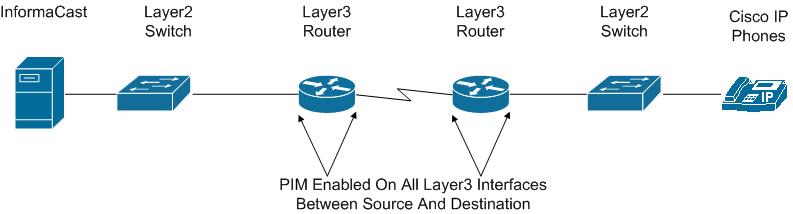
The following graphic shows an interface before PIM is properly configured and that same interface applying PIM.
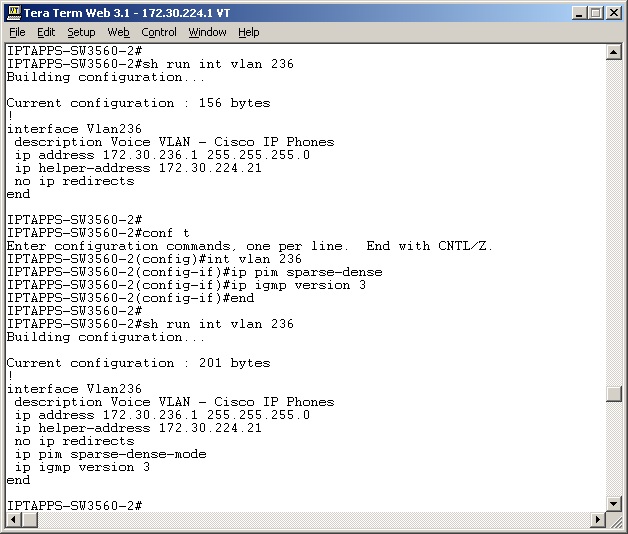
Back to Top
Audio Across WAN Links: GRE Tunnels/Paging Gateway
When InformaCast audio broadcasts are successful at the same location where the InformaCast server is located, but remote locations do not receive the audio, that indicates that the multicast audio traffic is not routing across the WAN link. Many circuit providers do not route multicast traffic across their MPLS networks; please check with your circuit provider to see if they will route your multicast.
When the circuit provider will not route multicast, there are two options to get the traffic to the remote sites:
- Create GRE tunnels from the hub location to the spoke locations to carry the multicast traffic
- Use the Singlewire Paging Gateway (sales@singlewire.com)
GRE Tunnels
Using your network, you can configure a GRE tunnel to carry your multicast traffic from the location where the InformaCast server is located to the remote site(s). The only traffic that needs to traverse these GRE tunnels is the multicast traffic you might want to route. The tunnels do not need to create a full mesh between sites, but only need to be configured from the hub to the spoke. The following graphic shows hub and spoke GRE tunnels that will route InformaCast’s audio traffic.
Cisco has detailed documentation to configure multicast over GRE tunnels, see http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk828/technologies_configuration_example09186a00801a5aa2.shtml
The advantages of using GRE tunnels to route multicast are:
- Administration. All configurations are done on network devices. This is a mature technology that is well documented and supported by network vendors. Once the initial configuration is completed, the ongoing administration is minimal.
- Cost. Because there will already be a router at both the hub and spoke locations, there is no additional hardware or software costs.
- Additional Functionality. GRE tunnels can also be used to carry other multicast traffic if desired, such as a centralized music on hold service.
The disadvantages of using GRE tunnels to route multicast are:
- Bandwidth. During an InformaCast broadcast, a G.711 µlaw audio stream will traverse the WAN link over the GRE tunnel. Most network design best practices specify G729 should be used on WAN links.
- Network Gear Overhead. While minimal, the encapsulation and decapsulation does require processing power from the network devices.
Singlewire Paging Gateway
The Singlewire Paging Gateway will allow a lower bit rate unicast audio stream to be sent from an InformaCast server at one location to a Paging Gateway across a WAN that isn’t routing multicast. The Paging Gateway can then turn the unicast audio stream it received from the InformaCast server at the other location into multicast on the local LAN segment.
For more information, please contact your Singlewire Territory Manager
The advantage of using a Paging Gateway to get audio over a non multicast enabled WAN is that the unicast audio stream travels over the WAN at a lower bit rate codec. At the remote site LAN, it is turned back into G.711 µlaw multicast.
The disadvantages of using a Paging Gateway to get audio over a non multicast enabled WAN are:
- Cost. The Paging Gateway will incur additional hardware and software costs.
- Ongoing Administration. Adding more devices and services around the network will require someone to administer those devices and ensure they are functional and current.
Back to Top
IGMP Snooping
IGMP snooping has been seen to cause issues with varying revisions of IOS on some Cisco switches. For this reason, if there are issues receiving the multicast audio stream at the phones, it would be worth testing without IGMP snooping configured on the switches where phones are connected. The following graphic illustrates where IGMP snooping should be turned off on the network.
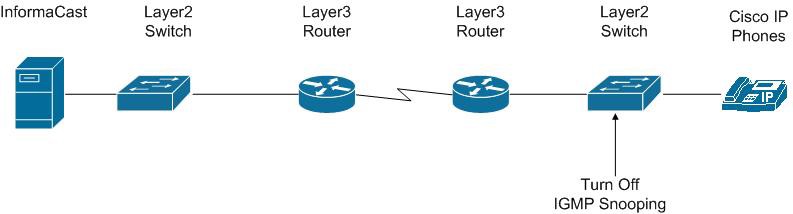
Back to Top
IGMPv3 and Newer Phone Models
Newer phone models are using IGMPv3 where earlier phone models used IGMPv2. This is important because by default IOS uses IGMPv2. If your network segment has a combination of older phones and newer phones, you may not perceive any issues. However, if a broadcast is sent only to devices using IGMPv3 on a network segment and the network has not been programmed for IGMPv3, the end result will be that multicast does not route to that network segment. The following graphic illustrates how the differences between IGMPv3 and IGMPv2 can affect your multicast traffic.
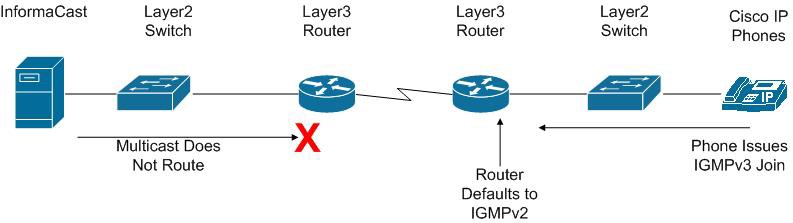
To verify if your phone(s) are using IGMPv3, you can take a network traffic capture using a protocol analyzer like Wireshark (see “Network Traffic Capture”). In the capture, the phone will issue an IGMP join to listen to the multicast audio.
The version of the IGMP join can be seen on the packet (circled in red in the following graphic).
To ensure multicast audio will route to network segments where the phones are using IGMPv3, the Layer 3 device must be programmed for IGMPv3. The following graphic shows an interface before and after configuring IGMPv3.
Back to Top
Download Multicast Considerations (pdf)




